Cell: smallest unit of life.

Nucleoid:a region of the cytoplasm that is not enclosed in a membrane sac.
Lipid Bilayer:is a continuous, oily boundary that prevents the free passage of water-solute substance across it.
Wavelength: is the distance from the peak of one wave to the peak behind it.
Electron microscope:use magnetic lenses to bend and diffract beams of electrons, which cannot be diffracted thought glass lens.

transmission electron microscope:electrons pass throught and specimen and are used to make images of its internal message.
Scanning Electron Microscope: direct a beam of electron back and forth across the surface of a specimen.

Organelles: Start out life with a nucleus and a membrane bounded sac.

Secretory Pathway: moves new polypeptide chains fom some ribosomes to ER or golgi bodies.

Endocytic Pathway: Moves ions and molecules into cytoplasm.

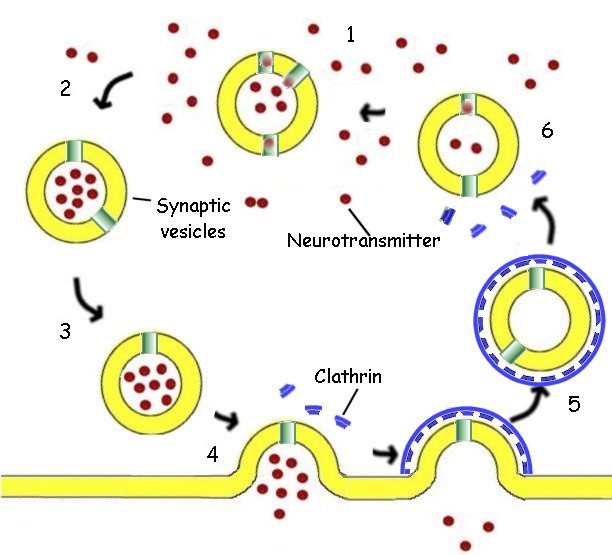
Vesicles: move substance fom one organelles to the next in life.
Nuclear Envelope: double-membrane system in which to lipid bilayers are press against each other.
Chromosomes: is a DNA molecules and its associated with proteins.

Chromatin: collection of DNA and all protein associated with it.

Cell Junction: molecules structue whee a cell send and recives signals.

Basal Body: barrel-shaped structue produces and organize microtubules into the 9+2 array,then it remains below the finished array.





No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario