
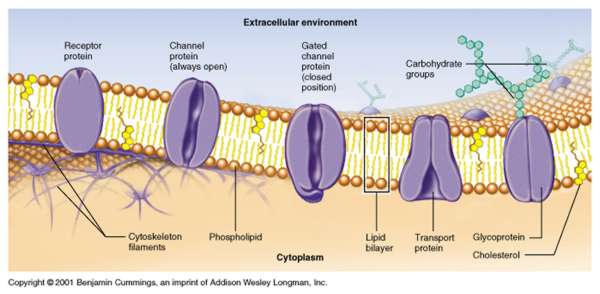
Receptor proteins: a bend extrcellular substance suchs as hormones that can triggern change in cell activity.

Recognition protein: identify tags for each species.
Adhesion protein: help cells of the same type locate each other and remaijns in the proper tissue.

Concentration gradient: a difference in the number per unit volume molecules of a substance between two adjoining regions.
Phagocytosis:is a common endocytic pathway.


Endocytosis: a small patch of plasma membrane balloons inward and pinches off inside the cytoplasm.

Osmotic pressure: one measure of the of the tendency of water to follow its water concentration gradient and move into that fluid.
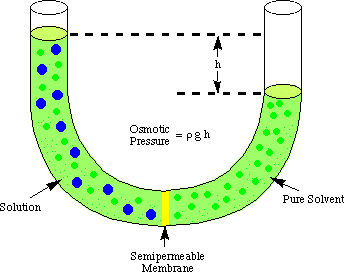
Hydrostatic pressure: fluid exerts against the wall or membrane that contains it.

Isotonic solution: show no net osmotic movement.

Osmosis: is the diffusion of water across the selectively permeable membrane to a region where the water concentration is lower.

Hypertonic solution: the one having more solute.

Hypotonic solution: it’s the one with fewer solutes.

Pressure gradient: is a difference in pressure exerted per unit volume between two adjoining regions.
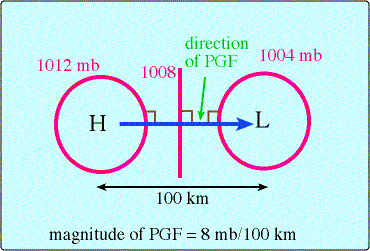
Electric gradient: is a simply difference in electric charge between adjoining regions.
Diffusion: the net movement of like molecules or ions down the concentration gradient.

Active transporters: pump a solute across the membrane to the sides where it is more concentrated and less likely to move on its own.

Transport protein: let specific solute diffuse through a membrane-spanning channel in their interior or actively pump them through.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario